Introduction
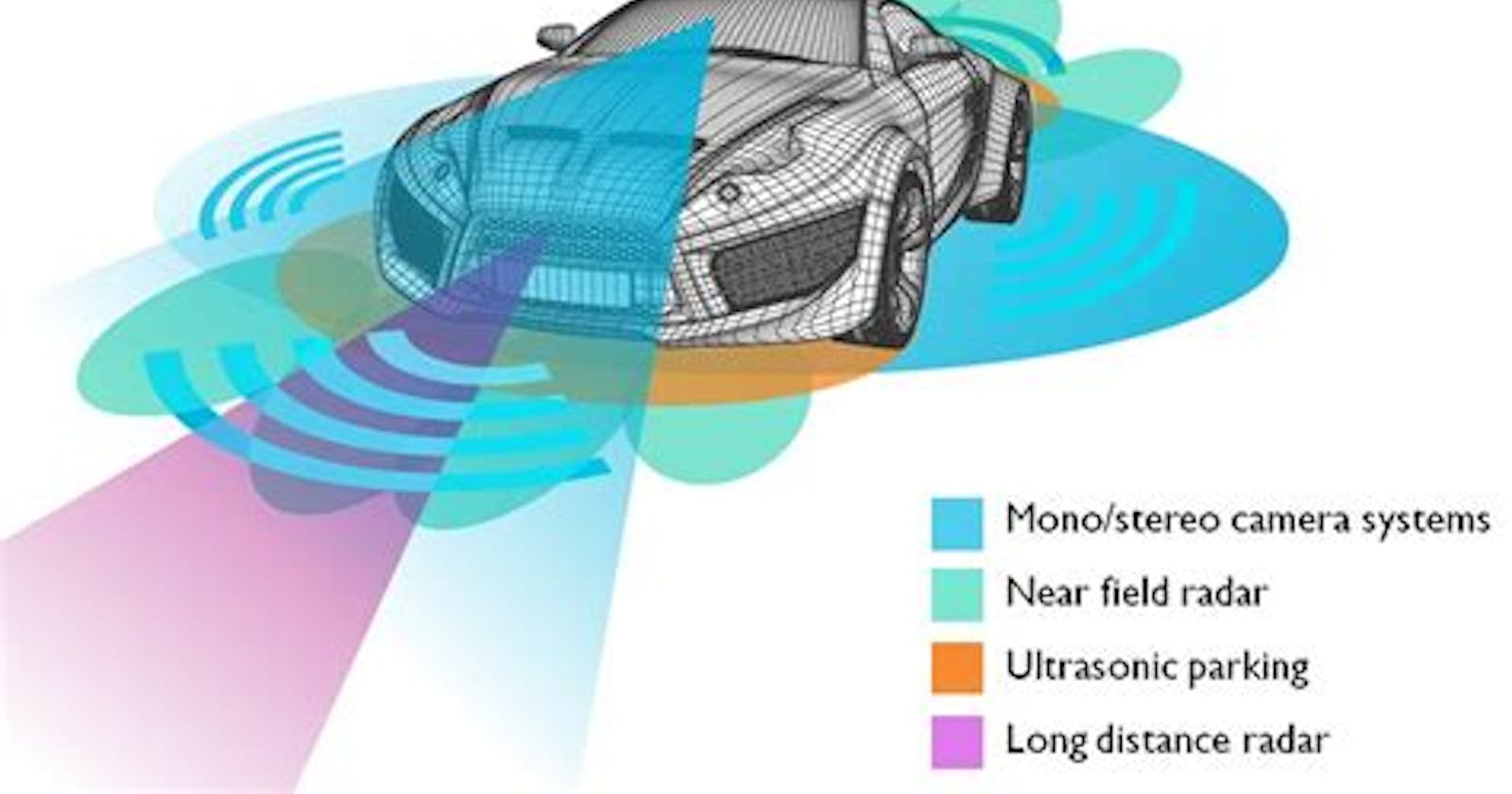
There are various sensors used in implementing the ADAS system. This blog is all about which sensors are and how they are used in the ADAS system. First of all, ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance System. To know in detail about what ADAS is, you can refer to my blog for more understanding.
Types of Sensors
Automotive Radar
Camera
Ultrasonic Sensors
Lidar
GNSS
GPS
IMU
This blog post is dedicated to understanding What is RADAR, its working, and its applications. The remaining Sensors are covered in subsequent blog posts.
Automotive RADAR
What is RADAR?
RADAR - Radio Detection And Ranging.
Radio - uses Electromagnetic waves in the radio spectrum
Detection - detect objects/targets like planes, cars, pedestrians, etc.
Ranging - calculates the range of the target from the sensor
Automotive Radar sensors (operating frequency)
24 GHz with small bandwidth
76-77 GHz with medium bandwidth
77-81 GHz with large bandwidth
Below is Radar manufactured by Continental.

Generally, Radar is installed behind the body of a vehicle because if Radar is installed on the body, then it will not give a good look to the vehicle.
The automotive radar sensor is also called the mm-Wave Radar sensor.
Working of RADAR
Automotive Radar was not invented for automotive but it was used at very high levels during world war to track fighter planes during the war.
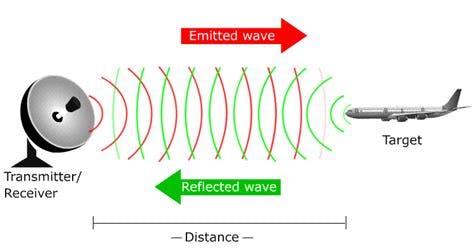
There is a transmitter and receiver at the same place, the transmitter sends out waves and whenever the target comes across the waves those waves get reflected in the radar receiver.
From RADAR, we get a list of points that are used to detect and track objects around the vehicle.
Let's say we get a list of points for detected objects which shows how far the object is, what is the angle, what is the velocity/speed and there are also other parameters such as RCS (Radar Cross Section), etc.
Classification of Radar - Based on signal processing
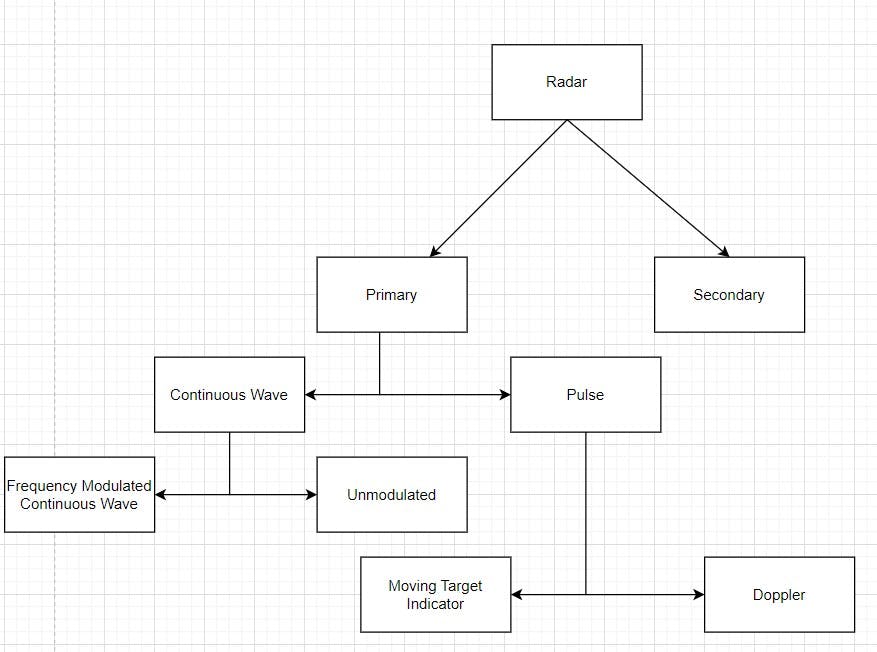
In modulated, there are many variants but a popular one is Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW). Most of the companies in the Automotive Industry are using this type of Radar.
Pulse technology is used more extensively in aerial applications because pulse technology can cover larger distances, and when any application requires a lesser distance then FMCW technology is used i.e. in the automotive industry.
Radar FoV
Field of View
The field of View is the total area covered by the sensor, where it can detect objects.
Main parameters which govern FoV of radar sensors:
2D FoV
Minimum and Maximum Range
Minimum and Maximum Horizontal Angle
3D FoV
Minimum and Maximum Range
Minimum and Maximum Horizontal Angle
Minimum and Maximum Vertical Angle
Below are the types of radars, their range, and their opening angle.
| Radar Type | Distance Covered | Opening Angle |
| SRR (Short range Radar) | 50m | Wide |
| MRR (Medium range Radar) | 80-100m | Wide to medium |
| LRR (Long range Radar) | 250 - 300 m | Narrow |
Generally, Long-Range Radar is used in implementing the Adaptive Cruise Control function in ADAS because it covers the long-range, and in Lane, it has to cover the target vehicle which is way ahead of the ego vehicle.
Why RADAR?
Functional Advantages
Radar can measure the relative speed of the target object (pedestrian, vehicle) on road in one measurement using the doppler effect.
RADAR measures the distance and angle of the target object.
Measures Radar Cross Section (RCS) which helps to understand the type of object.
Good performance in bad weather conditions like fog, rain, snow, etc whereas the camera will go blind in such weather conditions or image capturing quality will be less.
Good performance in different light conditions like day, night, evening, etc, because RADAR does not affect light as it works on the principles of Radio waves which have no connections with light.
Available in different ranges, angles, and speed coverage.
Physical Advantages
Normally, RADAR uses 77 GHz or sometimes from 77 GHz - 81 GHz, due to this we get a very small wavelength.
Wavelength can be calculated using the below formula
$$c = n * \lambda$$
where c is the speed of light and n is frequencies and the other is the wavelength.
So due to the small wavelength, we can design a small antenna and hence we can have a very compact size sensor.
RADAR waves can easily pass through plastic and similar material, so they can be mounted behind the actual body of the vehicle.
Low cost of production, hence we can use multiple sensors in one vehicle so we can enable 360-degree FoV.
In RADAR, there is no moving part involved, hence construction is robust.
Easy interfacing for measurement and diagnostic using Flex ray, CAN, ethernet, etc.
Applications of RADAR in ADAS
RADAR is most extensively used in Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) function in ADAS but below are the other applications in ADAS where RADAR is used including ACC.
Adaptive Cruise Control
Forward Collision Warning / Avoidance
Forward Cross Traffic Alert
Turn Assistance
Blind Spot Detection
Vehicle Exit Alert
Rear Cross Traffic Alert